All You Need to Know about the COVID-19 Cytokine Storm
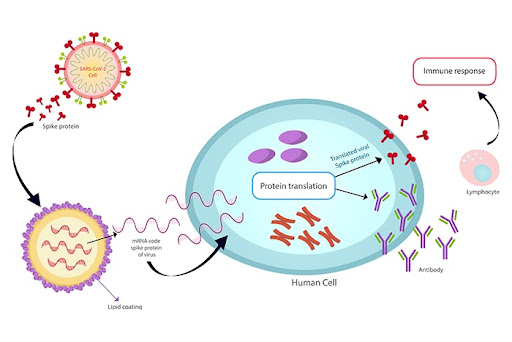
COVID-19 is a swiftly spreading global threat declared a pandemic by the WHO. Coronavirus is transmitted via droplets or unmediated contact. It infects the respiratory tract resulting in pneumonia in most situations and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in around 20 % of cases. Fatality in COVID-19 patients has been linked to the proximity of the so-called “cytokine storm” coaxed by the virus.
Excessive production of proinflammatory cytokines influences ARDS aggravation and widespread tissue degeneration failing multi-organ and death and targeting it. At the same time, the supervision of COVID-19 patients could improve survival percentages and diminish mortality percentages.
What is a Cytokine Storm?
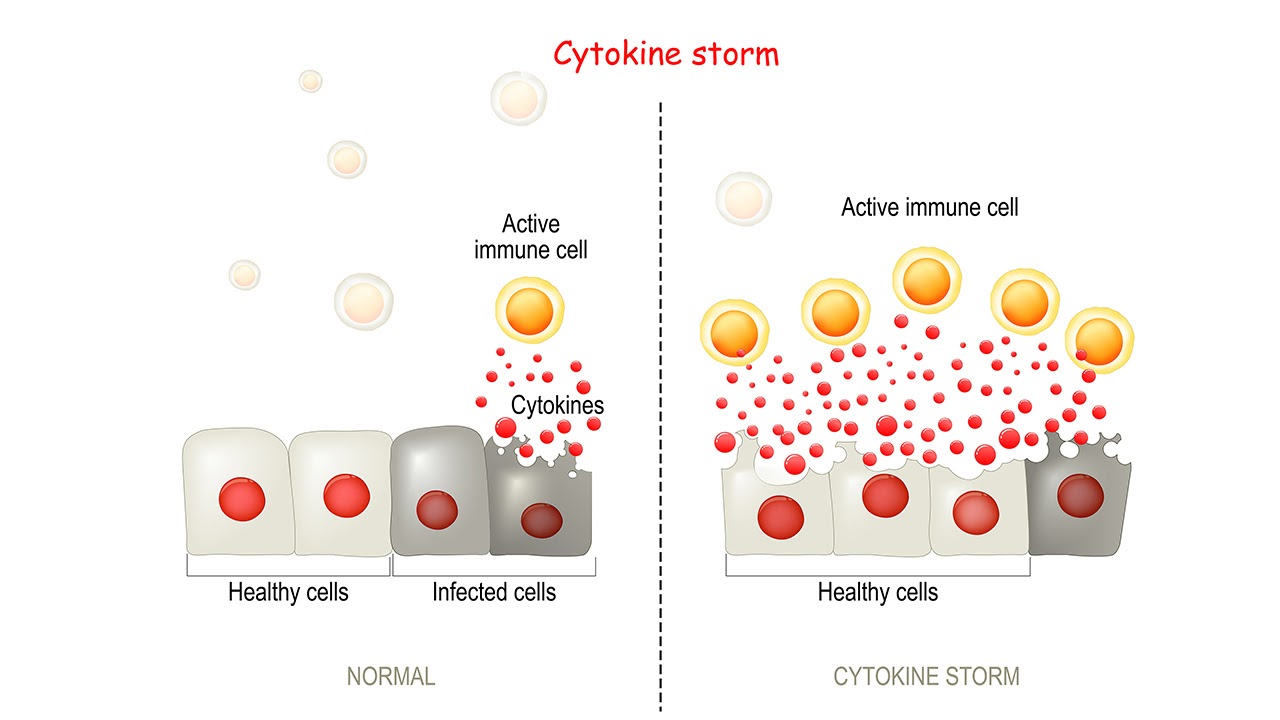
When laymen hear the word “storm,” they think of rain or downpour, but that’s not an accurate way to describe a cytokine storm. Clinically speaking, it indicates that a cell line has been turned on, leading to the production of several biological mediators that induce changes to the body and meddle with normal cell proliferation.
Generally, this means a disproportionate number of cytokines are released, which create high levels of inflammation and results in the body being flooded—so much inflammation that it can be deadly.
When a healthy body is combating an infection, there occurs a natural immune system acknowledgement. Part of this response involves releasing cytokines and biological chemicals that stimulate cell lines and communication between cell cultures.
These cytokines typically signal the regulating immune system to start doing its normal job, except this flow suddenly becomes much more stimulated. Ordinarily, cytokines are essential to humans in moderation, but when bind to a specific pathway that is engaged too much, the regulating immune system begins to cause damage to the patient.
Are Cytokine Storms Occurring In COVID-19 Patients?
Yes, and scientists aren’t surprised. Cytokine storms can instigate several infections, including pneumonia, influenza, and sepsis. This heightened immune response does not happen in all patients with severe conditions, obviously, but specialists do not know what makes people more responsive than others. That is particularly true with COVID-19 because we know so little about how it works.
Transmission and Clinical Indications Of COVID-19
COVID-19 is affected by the SARS-CoV-2 that pertains to the beta-coronaviruses subfamily. Positive single-stranded giant RNA viruses surround coronaviruses. Although the first data ready about COVID-19 by epidemiological data and studies intimates possible animal-to-human synchromesh by wild animals.
After that, reports have increasingly illustrated that the virus spreads human-to-human through droplets or direct contact, stating that individuals who did not have direct touch were diagnosed with COVID-19. Secondary cases were rising swiftly at hospitals amidst health care workers who had protracted contact with COVID-19 patients.
The virus was confirmed to increase through respiratory droplets from coughs/ sneezes, with the capability of the host to emit the virus while asymptomatic. Studies are now also intending the possible faecal-oral transmission of the virus. Although many cases of COVID-19 remain asymptomatic, some patients get pneumonia, and 10% of cases necessitate ICU admission and mechanical ventilation.
The Cytokine Storm and its Profile
The newly emerged COVID-19 virus is continuing to threaten medical health systems worldwide, and the situation is still becoming more detrimental than before. The COVID-19 postures an increasing menace to humans. COVID-19 infection is characterised by an aggressive inflammatory response with the release of many proinflammatory cytokines in effect identified as “cytokine storm.”
Interferons are glycoproteins composed of a wide variety of cells in response to infection. Interferons and Interleukins are a combination of cytokines that play vital roles in the proliferation, maturation, activation, and differentiation of immune cells.
The organism immune reaction to the SARS-CoV-2 virus is high-strung, resulting in an excessive inflammatory response. Several studies analysing factors and cytokine profiles from COVID-19 patients suggested that the cytokine storm correlated directly with lung injury, multi-organ failure, and unfavourable prognosis of severe COVID-19.
The immune system has an impeccable mechanism capable of responding to diverse pathogens. The typical antiviral immune response needs the activation of the inflammatory cell signaling pathways of the immune system; nevertheless, the unusual reaction of the host’s immune system can cause severe disease if it persists unchecked. It is an essential part of inflammatory development. Cytokines antibodies are created by several immune cells, including innate macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and the adaptive T and B lymphocytes.
Cytokine Storms have been recorded in several viral infections, including influenza H5N1 virus, influenza H1N1 virus, and the two coronaviruses related to COVID-19; SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. The chief contributors to the reciprocation of the cytokine storm are IL-6 and TNF-α or tumour necrosis factor alpha . In the inadequacy of an immediate and appropriate therapeutic invasion, patients contract ARDS because of acute lung damage accompanied by multi-organ failure following death. Hence, individuals should treat it immediately; otherwise, it may result in mortality.
The early recognition of the storm and the timely treatment can lead to a better outcome. Numerous biological agents targeting cytokines proteins have been proposed for employing cytokine storms; it seems to be one of the probable causes of mortality in the latterly declared pandemic of COVID-19. Remedial approaches to managing the COVID-19 cytokine storm might present an avenue to minimise COVID-19 related morbidity and mortality.
Possible Treatments for Cytokine Storm in COVID-19
Cytokine Adsorption Device
Cytokine adsorption includes using a method, such as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), to filter harmful substances quickly. An extracorporeal cytokine hemoadsorption device called Cytosorb captures and reduces inflammatory mediators. The plasma level of IL-6 and procalcitonin decreased in patients with intractable ARDS after treatment with ECMO utilising a hemoadsorption device. Moreover, it can gain hemodynamic stabilisation, respiratory recovery, and deterioration in capillary leakage in combination therapy.
A similar therapy requires dialysis. The primary water-soluble arbitrators are removed from plasma, and the hemofilter can have calculated adsorptive properties. Continuous venovenous hemofiltration and adsorption for harsh septic shock are being tested.
A GM-CSF receptor blockade is undoubtedly a potential option for the treatment of more critical subsets of COVID-19, and more comprehensive studies are guaranteed to confirm the role of GM-CSF in the pathogenesis of cytokine release syndrome.
Neutralising unbalanced cytokine proteins with hemoadsorption devices might be relatively effective. The drawback is corticosteroids: a broad range of cytokines would be adsorbed- therefore, it would point to the absence at a reasonable or still insufficient level. We suggest tending to the cytokine storm in COVID-19 based on cytokines and chemokines’ lab results. Meantime, adjusting the parameters of the devices for restricting overtreatment.
Visit our website to buy cytokine antibodies; contact Helvetica Health Care for further information.